This project was developed during my Master’s research at Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, under the supervision of Dr. Carlos Eduardo Pereira .Two papers were generated from this research:
- Ontological User Modeling for Ambient Assisted Living Service Personalization, presented at The 5th IFIP International Embedded Systems Symposium, 2015
- A Service Personalization System for Smart Homes Based on Semantic Web and Multi-Agents, (accepted but not published due lack of funding) to the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Smart Internet of Things
Overview
Given the fact that at least 80% of people older than 60 are living with one chronic illness and 64% of older adults prefer to stay in the comfort of their own homes, it is essential to develop technologies that help older adults not only to age, but also live in place i.e., independently and comfortably in their homes [3].
This work proposes a service personalization system based on the Semantic Web technologies and the multi-agent paradigm aimed to provide personalized assistance to people with disabilities and functional limitations within a smart home setting. In the proposed system, user’s characteristics are represented through an ontological user model and a rule-based reasoning mechanism is used to infer additional information needed for tailoring the services available in the environment. The multi-agent paradigm is used to create a scalable, flexible, and distributed architecture where the agents use the user model and the reasoning mechanism to accomplish specific roles. The proposed system was validated through its integration with a Service Oriented Architecture and a demonstration of its use in three standard use cases.
System demonstration
a) Infrastructure
Since a full smart-home facility was not available during this work development, a hybrid infrastructure composed by a simulator linked to a commercial automation was utilized. The simulation software has four main functions:
- To allow the management and simulation of virtual devices;
- To communicate with the Service Oriented Architecture to get the state of all real and virtual devices;
- To display the state of all devices in a graphic interface, similar to a supervisory system;
- To simulate a person that can be moved through the simulated house.
Using this software, a scenario based on the DOMUS lab smart-home was created. The devices employed and their distribution are described bellow:
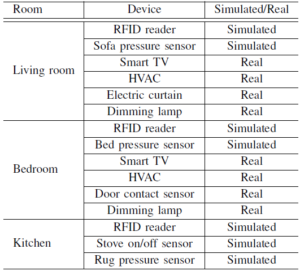
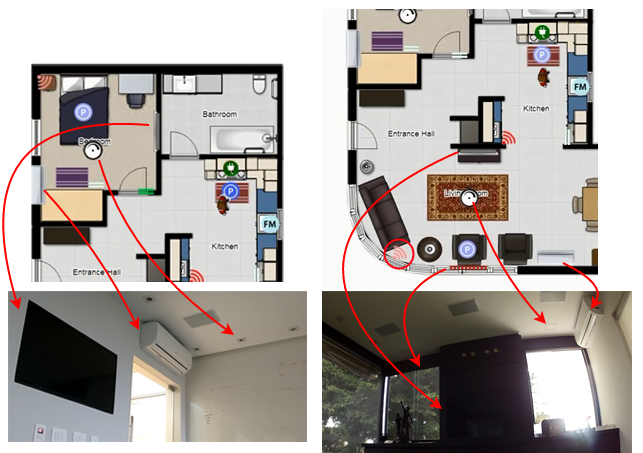
b) Users
Two fictitious users were defined based on the results of the project “Action Aimed at Promoting Standards and Interoperability in the Field of AAL”
- Jane Miller is an 85-year old lady who still lives independently in her own apartment. Despite several chronic diseases that require her to take many different drugs three times a day, she is doing relatively well. However, recently she has started to forget things and make mistakes that were unheard of before. The family doctor has diagnosed her with a mild cognitive impairment that may or may not worsen over time. A few months ago she switched on the cooker, forgot about it, and went shopping. The cooker caused a fire in the kitchen that could well have burned down the house.
- Peter is a 83-year old person living in the suburbs of a big Brazilian city. His wife died 4 years ago and his son has moved to another city about 200 km away.In the past he never got used to computers and mobiles but since the new generation of smartphones and tablets with touch screen have been available, he is more keen on technology. One of the main difficulties in Peter’s daily life is to read small texts and images displayed on his Smart TV and smartphone. Furthermore, Peter has a mild listening difficulty.
c) Use case 1
.
Using the simulation software, Jane Miller’s character is moved to the kitchen, turns on the stove and then goes to her bedroom. In the moment she enters the bedroom, the lighting is adjusted to 50% and the temperature is set to 22 °C, according to her preferences stored in her ontological user profile.
After that moment, two scenarios are reproduced:
a) Jane closes the bedroom door and sits in a chair to read a book. After a few minutes the system issues an alert to notify Jane about the dangerous situation. The alert is delivered according to her preferences inferred by the reasoning process – in this case, since she has a severe hearing impairment, the alert is delivered though a
text message in the Smart TV. This message is displayed in her language (English) and with a font size inferred from her visual capability information.
b) Jane closes the bedroom door and lays in her bed to get some rest. Since Jane adjusted the bedroom lighting to 10% a few days ago during the same situation, now the system automatically adjust the bedroom lighting to this value every time she closes the door and lays in the bed. In addition, the temperature is changed to 18 °C due the context-dependent preferences inferred. After a few minutes, the system identifies the danger situation and acts in order to keep Jane safe – since she is sleeping, the system sets the bedroom lighting to a maximum level and reproduces the sound message ”‘Attention! You forgot to turn off the stove!”’ using a volume level of 80% (value inferred based on her listening capability level).
When the same situations were reproduced with the user Peter, the message alerting the stove was left on was presented through an audio in Portuguese, since this is the only language spoken by Peter. Moreover, the audio was reproduced using the volume level inferred based on his listening capabilities.
d) Use case 2
.
In this use case, Jane goes to the kitchen, turn on the stove and goes to the living room, where the lighting and temperature are properly adjusted according to her preferences. Then, she uses an AAL application installed in her smart phone to request a movie to be played on the closest Smart TV and sits on the sofa. The movie is reproduced using the language, volume level, screen contrast and brightness according to the preferences inferred from her capabilities information. At this moment, the system identifies her new context and adjust the lighting to improve her comfort. After a few minutes, the system identifies the dangerous situations and issue an alert message in the same Smart TV she is watching the movie . Again, the text size and the language were inferred by the profile manager based on her personal information.
